Knee
The knee moves vertically along ways machined into the column. The knee supports the table via the saddle. The knee is positioned vertically via the knee elevating crank shown below.
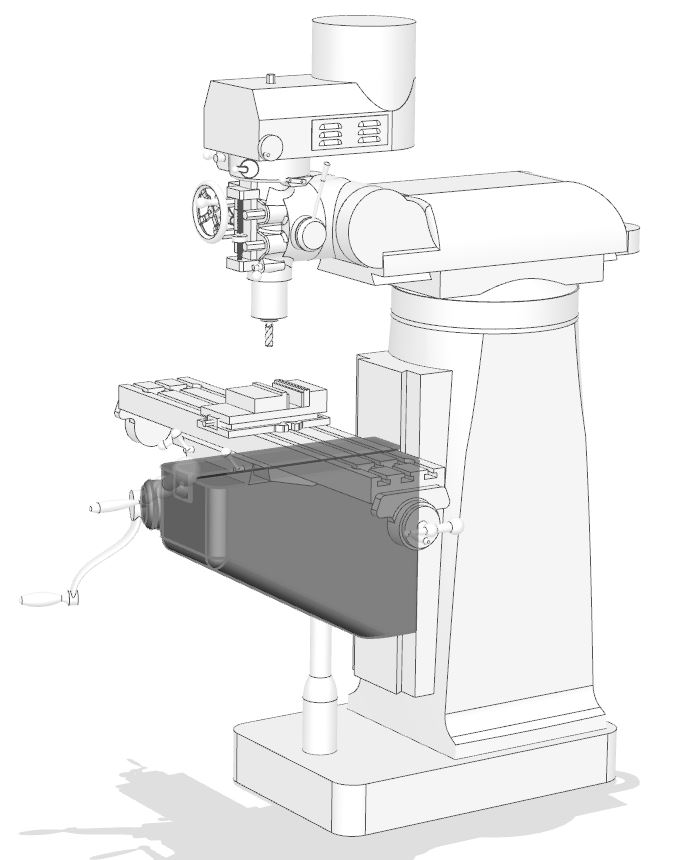
Knee Elevating Crank
The knee elevating crank (or knee handle) raises and lowers the knee, and hence the work mounted on the table. The knee elevating crank is the most rigid way to make adjustments in the vertical direction. The quill (located in the head) is another way to make adjustments in the vertical direction. The vertical direction is often referred to as the Z axis.
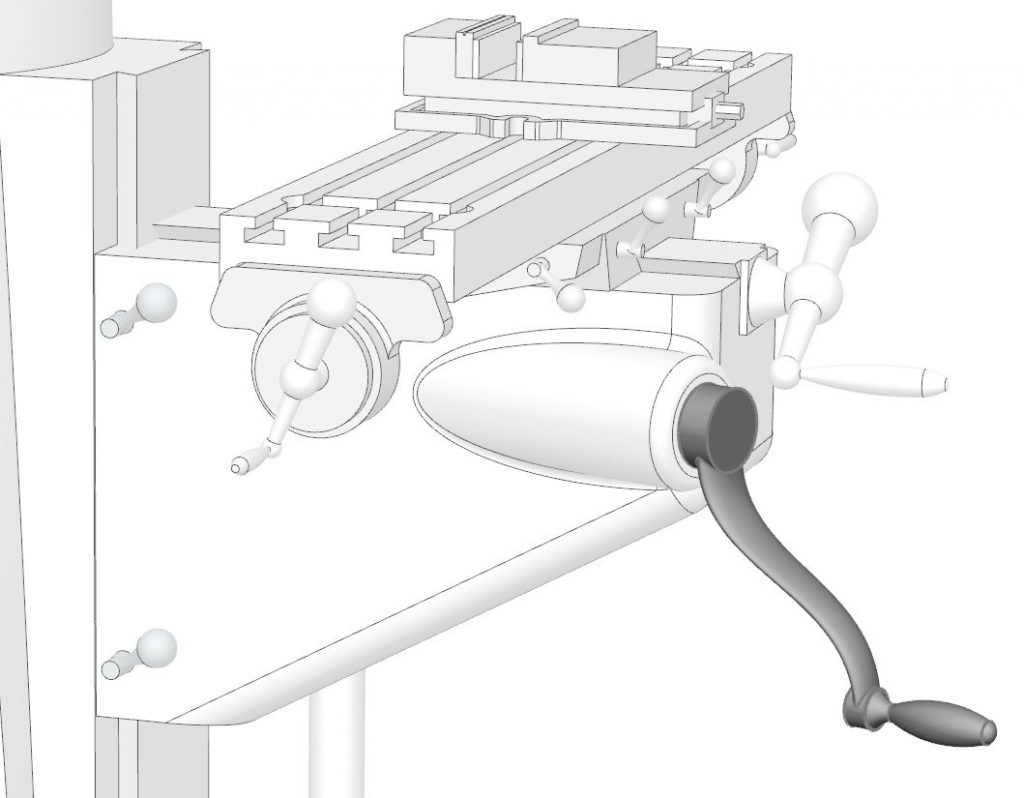
Knee Locks
Knee locks provide a way to hold the knee rigidly in position.
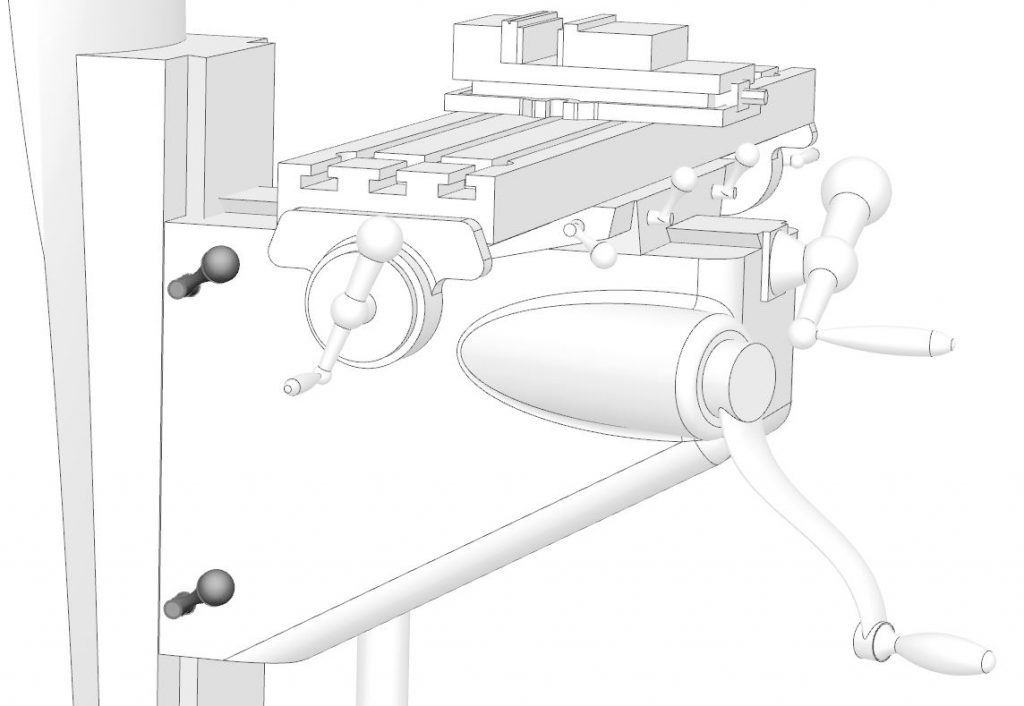
Cross Traverse Crank
Also called the cross feed handle or saddle traverse handle, the cross traverse crank moves the table in and out relative to the operator. This direction of motion is often referred to as the Y axis.


Recent Comments