First the photoresist is applied to the substrate to be etched. Photoresist can be applied by the following methods:
- Lamination
- Spin coating
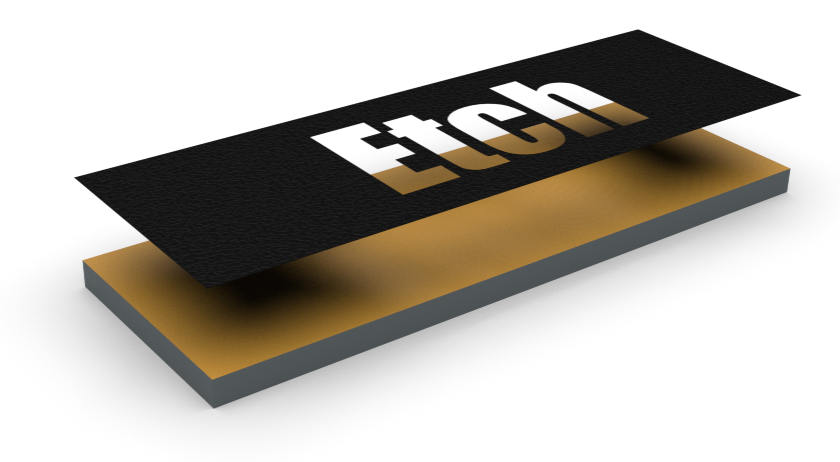
A photo tool or mask is created.
Masks can be
- Positive development
- Maskant (photoresist) becomes more soluble after exposure
- The unexposed areas are not dissolved in the development process.
- Negative development
- Maskant become less soluble after exposure
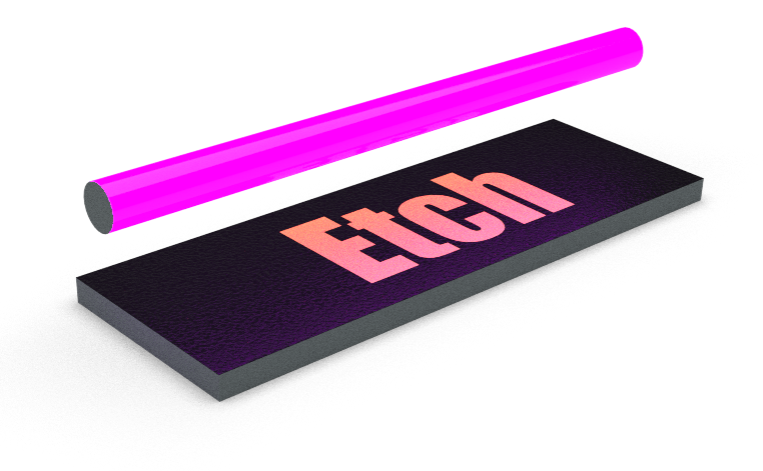
Photoresist is exposed to UV light.
A latent image is created. In this case, the exposed area will become more soluble when developed.
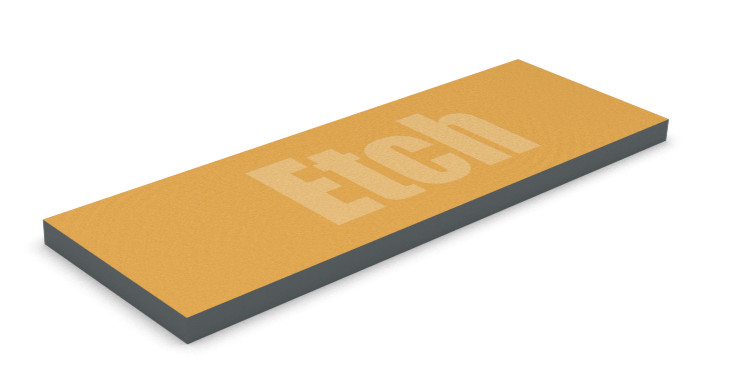
The resist is developed and the undeveloped resist is washed away.
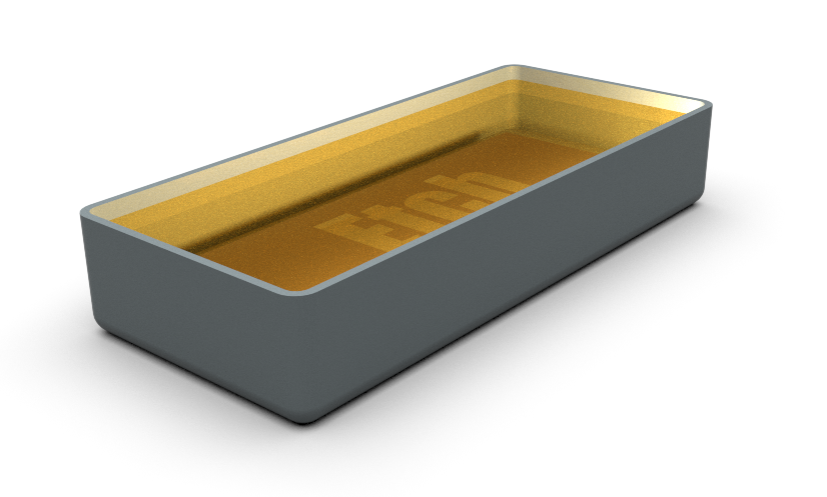
The developed resist is now ready for etching.

The exposed areas are etched away by the etchant solution and the mask is washed away.

The workpiece is then ready for other processes.
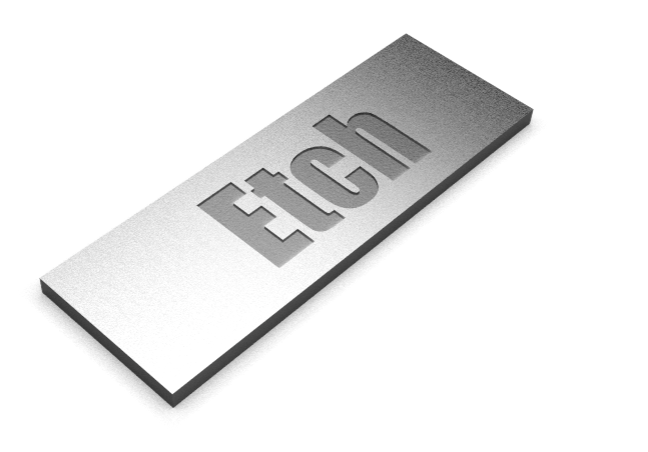
Example application: Signage. Etched areas can be filled with paint.


Recent Comments