Thread form refers to the profile of a screw thread. Thread standards that define thread form, series, class, allowance, tolerance and designation are usually issued by thread form.
Note: Methods of designating screw threads varies by standard. Refer to the individual standard for proper specification of screw thread requirements.
Examples
Sharp V
Sharp V threads were used in until about 1909. Sharp V threads had the disadvantages of being hard to produce and easily damaged. One advantage is that a single cutting tool can produce a variety of pitches because of the sharp root.
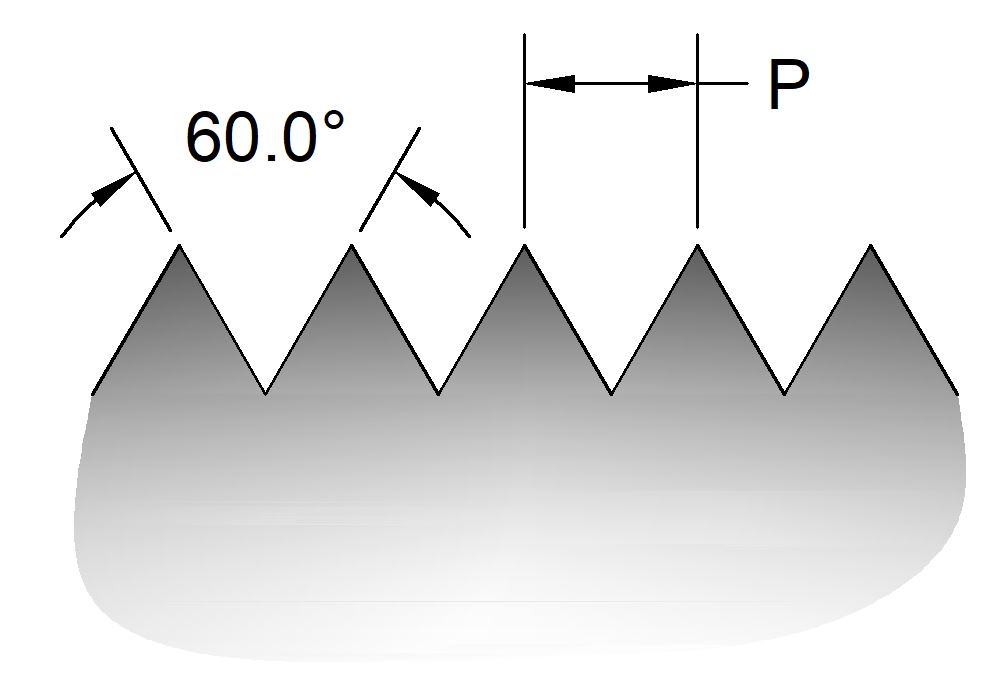
Unified
Unified threads are among the most common thread form used in the United States. There are several series of unified threads. The basic profile is shown here.
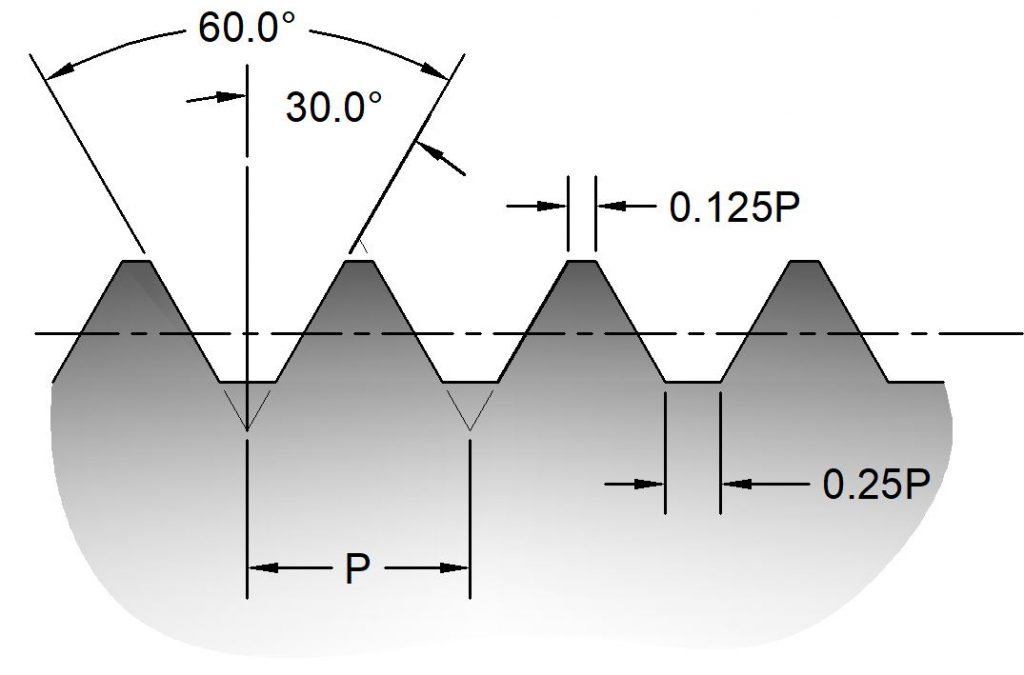
ACME
ACME threads are commonly used in power transmission application such as in lead screws. ACME threads are similar to European DIN103 trapezoidal threads, but they are not interchangeable.
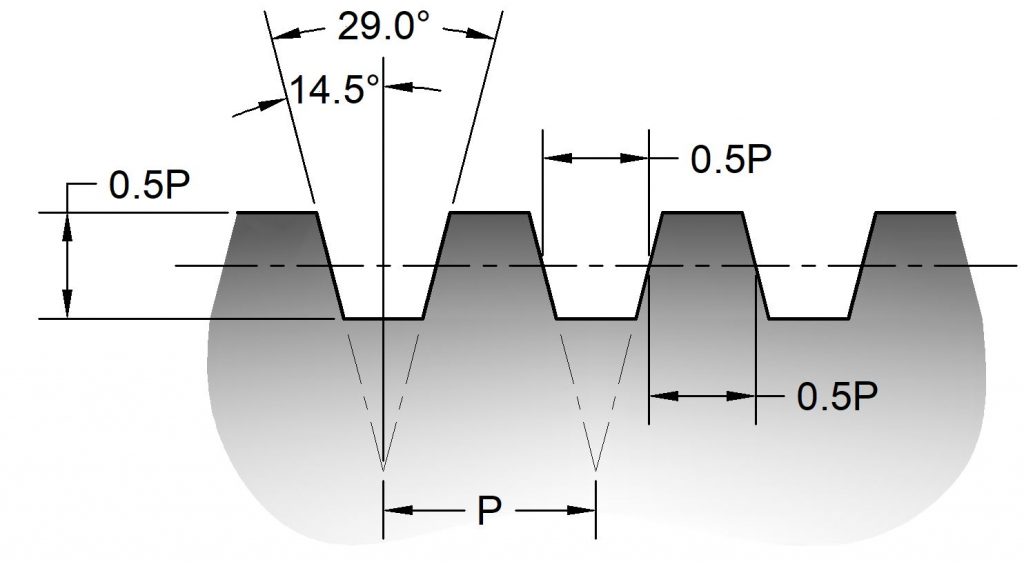
Buttress
Buttress threads are used when force will be applied in one direction more than the other. For example, in leadscrews for clamping operations. There are several versions of buttress threads in use today including ANSI B1.9, British standard buttress threads, and the Löwenhertz thread.
Buttress threads are available in either pull (BUTT) or push (PUSH-BUTT) configuration.
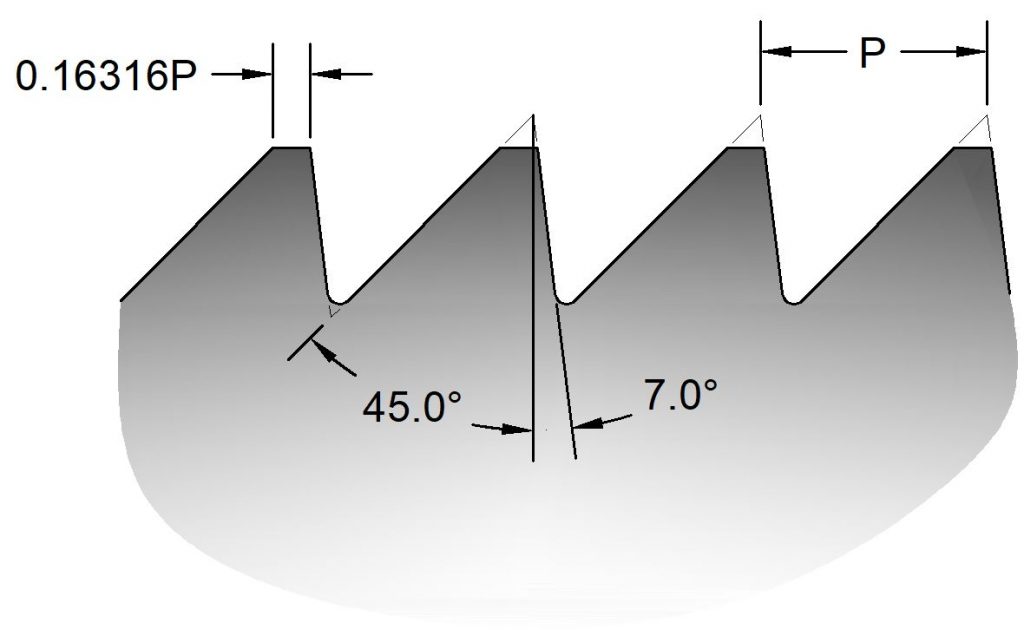
Lamp Base
The “American Standard” lamp base thread is designed to be rolled into sheet metal components.
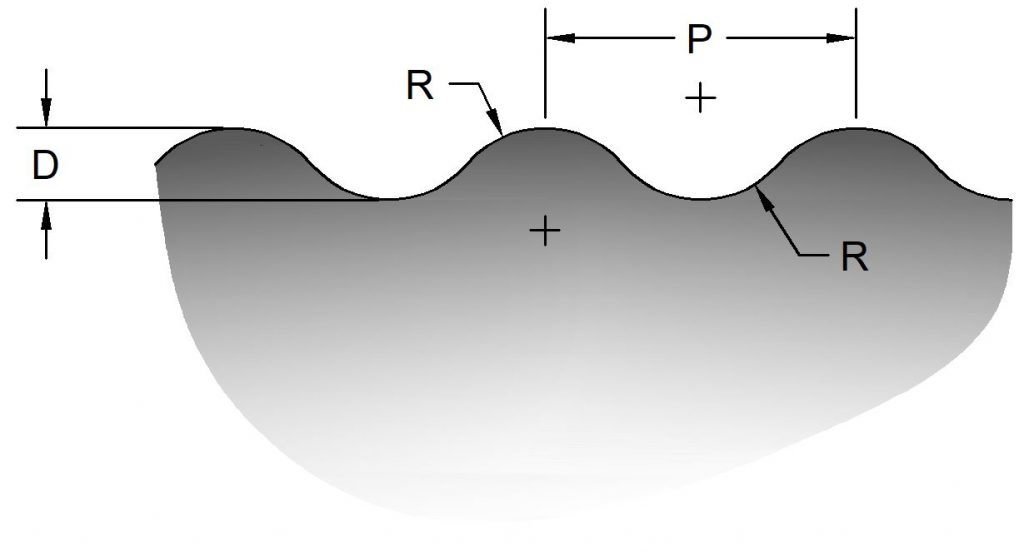
Basic Profile
Most o the images shown above are of each thread form’s basic form. Actual thread dimensions are determined by the allowance (usually clearance between the external and internal threads) and the amount of tolerance as it deviates from the basic profile.
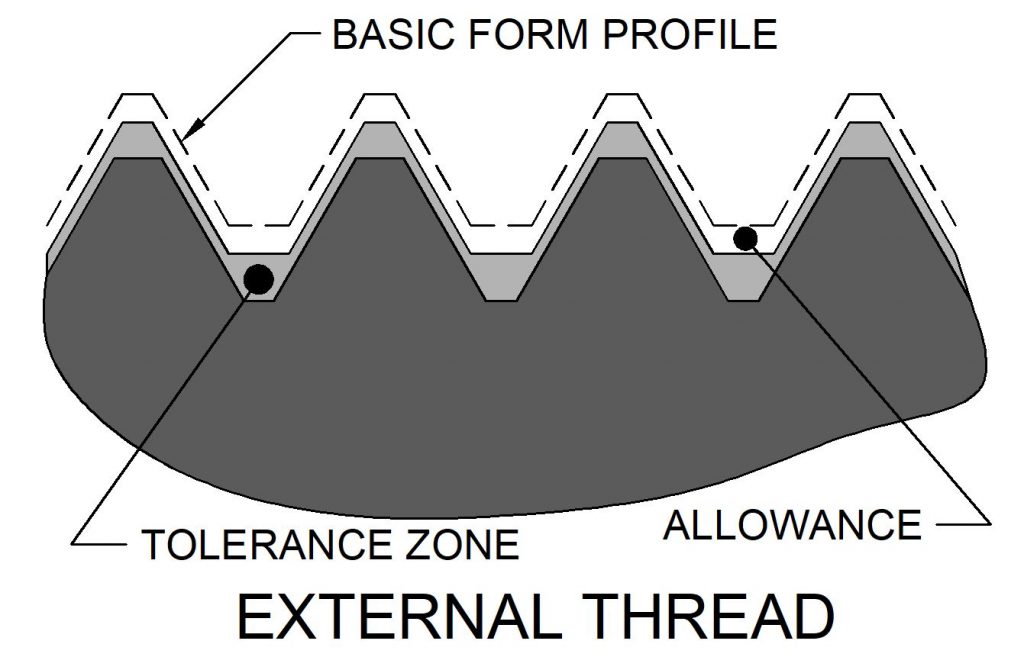
Examples of Various Thread Forms and Standards
| Symbol | Standard | Description |
| ACME | ASME/ASME B1.5 | ACME Thread Form (ACME-G, General; ACME-C, Self-Centering) STUB ACME (B1.8) |
| AMO | ANSI/ASME B1.11 | American Standard Microscope Objective Thread |
| BUTT | ANSI/ASME B1.9 | Buttress Threads (PUSH-BUTT, Push type) |
| M | ANSI/ASME B1.13 | Metric Screw Threads MJ – (B1.21M) |
| NH | ANSI/ASME B1.20.7 | Hose Coupling Threads NHR- for garden hose applications |
| NP | ANSI/ASME B1.20.1 ANSI/ASME B1.20.3 | American Standard Pipe threads – Various. Includes: NPS for straight threads, NPT for tapered threads, PTF for dryseal. |
| UN | ANSI/ASME B1.1 | Unified. Various. Includes: UN – Constant-pitch series UNC – Coarse-pitch series UNF – Fine-pitch series and others. UNJ – Rounded root (B1.15) UNR – Rounded root UNM – Miniature (B1.10) UNS – Special and more… |
| DIN 405 | Knuckle | |
| DIN 780 | Worm | |
| DIN 13 | Metric ISO V thread | |
| Whitworth thread |


Recent Comments